Ergonomic Principles In The Design Of Hand Tools
Weight of the tool
Ideally, a worker should be able to operate a tool with one hand. The weight of the tool may depend on the use:
- 2.3 kg (5 lb) if the hand tool will be used away from the body or above shoulder height.
- 0.4kg (1 lb) for precision tools to allow for good control.
Tools above these recommendations should be supported with a counterbalance.
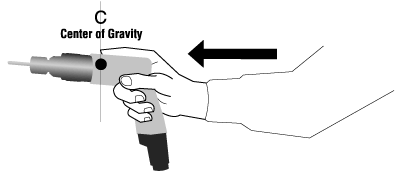
Figure 1
It is also important that the centre of gravity be aligned with the centre of the gripping hand. In other words, tools should feel "easy" to hold either in an upright position or in the position it will be used (i.e., pointing down). For example, drills that are "front-heavy" will require effort (especially in the wrist and forearm) to hold in a usable position and should be avoided. The exception to this principle is a power hand tool, such as a grinder, that has to be heavy in order to reduce the force that the worker has to exert while using it.
Handles
With the exception of tools for precision work (e.g., watchmaking, microsurgery, carving), the handles and grips of hand tools should be designed for a power grip. The belief that smaller tools should have smaller handles while larger tools have larger ones is debatable.
Handle shape
Tools with "bent" or angled handles or tools with pistol-grips are beneficial where the force is exerted in a straight line in the same direction as the straightened forearm and wrist, especially when the force must be applied horizontally (see Figures 2, 3, 4).
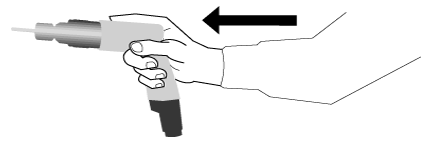
Figure 2
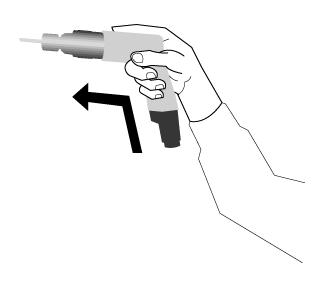
Figure 3
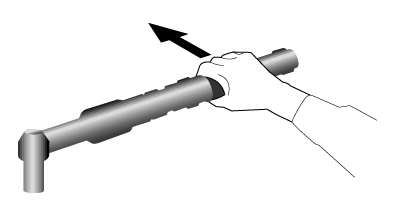
Figure 4
Tools with straight handles are for tasks where the force is exerted perpendicular to the straightened forearm and wrist, for instance, when the force must be applied vertically.
Shaped tools such as bent-handle tools are effective where most of the tasks are done in the same plane and height as the arm and hand, and when only one or two other tools are used (see Figure 5).
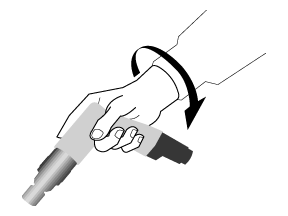
Figure 5
Knowing the tasks and the layout of the workplace where they will be used is vital for selecting the right tools for any given job. Select tools that do NOT require wrist flexion, extension or deviation. In other words, select tools that allow you to keep the wrist straight or in a neutral position.
The crucial ergonomic principle in tool use and design -- bend the tool, not the wrists -- however correct and valuable does not always prevent discomfort and injuries when bent-handle tools are used indiscriminately, regardless of the layout of the work situation.
Diameter
Handle diameter recommendations vary. In general, cylindrical handles at 40mm (1.5 in) offer a better power grip, with a range from 30-50mm (1.25 to 2 in). For precision grips, a diameter of 12mm (0.45 in) is recommended, with a range of 8-16mm (0.3 to 0.6 in). The larger diameter will allow for maximum torque, while the smaller diameter helps with dexterity and speed.
Length
A handle that is too short can cause unnecessary compression in the middle of the palm. It should extend across the entire breadth of the palm. Tool handles should be not less than 100 mm (4 in) to reduce the negative effects of any compression exerted. Handles around 120 mm (5 in) are generally recommended. Keep in mind that the use of gloves requires longer tool handles.
Separation between handles
Crushing, gripping or cutting tools such as pliers or tongs are equipped with two handles. The recommended distance separating the handles is between 65-90 mm (2.5 to 3.5 in). Grips that are larger than 100 mm (4 in) will be difficult for some users. Tools with larger or smaller spans will reduce one's maximum grip strength.
Materials and texture of handles
To ensure a good grip on a handle, sufficient friction must exist between the hand and the handle. This is particularly important where a considerable force must be applied with a sweaty hand. Hand tools should be made of non-slip, non-conductive and compressible materials. For example, textured rubber handles provide a good grip, reduce the effort needed to use the tool effectively, and prevent the tool from slipping out of the hand. Glossy coatings and highly polished handles should be avoided. The electrical and heat insulation properties of the handles are important for power hand tools. Handles made of plastics or compound rubber are recommended. Sharp edges and contours can be covered with cushioned tape to minimize lacerations.
The table below summarizes some of the guidelines presented above.
| Guidelines - Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Description | Guideline | Reason |
| Tool shape | Slightly contoured | Easy grip |
| Direction of force is in-line with forearm and wrist (typically horizontal) | Bent handle | Minimal wrist deviation |
| Direction of force is perpendicular to forearm and wrist (typically vertical) | Straight handle | Minimal wrist deviation |
| Separation distance between handles (for crushing, gripping or clipping tools such as pliers or tongs) | 65-90 mm (separation distance) | Maximum grip strength |
| Handle length | > 100 mm | Keep contact out of palm |
| Handle diameter (power grip) | 30-50 mm | Greater force and stability |
| Handle diameter (precision task) | 8-16 mm | Greater control |
| Material and texture of handles | Non-slip non-conductive materials | For comfort and reduces effort required to use tool |
Ergonomic Principles In The Design Of Hand Tools
Source: https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/ergonomics/handtools/tooldesign.html
Posted by: haleycouldic1973.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Ergonomic Principles In The Design Of Hand Tools"
Post a Comment